Ryu BGPSpeakerの実践活用へのチャレンジ 〜BGP/OpenFlow連携編〜
これまで、OpenFlow簡易ルータ作成を通じて、SDN/OpenFlow的な実装テクニックでも市販ルータ相当なIPルーティング制御が可能であることを確認してきました。しかしながら、これまでのOpenFlow簡易ルータでは、デフォルト・ルーティングしか対応していないため、市販ルータと比べてみるとルーティング機能面で、相当見劣りする現状だと思います。SDN/OpenFlow的な実装テクニックの学習素材と割り切る場合には、これで十分なんでしょうけど。
ところで、最近、Ryu SDN FrameworkにてBGPSpeaker機能が利用できるようになったようです。そこで、OpenFlow簡易ルータでも、BGP機能を取り込んだ上で、ルーティング機能拡充にチャレンジしてみます。
◆まずは、BGPSpeakerを試してみる
Ryu ドキュメントに記載されているBGP Speakerを動かしてみるところからはじめます。
BGP speaker library — Ryu 3.15 documentation
0. 目標感
「家庭LANとPC端末との間を、BGPSpeakerを介して接続した場合、PC端末〜インタネット回線までの途中経路区間でのルーティング情報の配布が正しく行えるかどうかを確認する。」という目標感で、動作環境を構築しました。
1. 動作環境
Ryu SDN FrameworkのBGPSpeaker機能を試してみるにあたり、BGPルータが必要となります。
市販のBGPルータを購入するほど、家計に余力がないので、極力安価に環境整備が実現できる方法として、OpenWRT化したBuffaloルータにQuaggaをインストールして対応しました。

Ryuコントローラは、以下のパッチ導入後のバージョンを配備する必要があります。必要に応じてアップデートを行ってください。
[bgp: bug fix of handling nexthop for eBGP peering · aa497ed · osrg/ryu · GitHub
2. BGPルータ(Quagga1)動作確認
以下のコンフィグ設定を行った上で、BGPテーブルを確認しておきます。
Quagga-1# sh run Building configuration... Current configuration: ! ! password zebra ! interface eth0 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface eth0.1 ip address 192.168.200.1/24 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface eth0.2 ip address 192.168.100.100/24 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface eth0.3 ip address 172.16.101.1/24 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface eth0.4 ip address 172.16.102.1/24 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface eth0.5 ipv6 nd suppress-ra ! interface lo ip address 10.0.0.1/32 ! router bgp 65001 bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 redistribute connected redistribute static neighbor 192.168.200.100 remote-as 65002 ! ip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.100.1 ! access-list vty permit 127.0.0.0/8 access-list vty deny any ! ip forwarding ipv6 forwarding ! line vty access-class vty ! end
BGPルータ(Quagga1)では、複数のPrefix経路情報がBGPテーブルに保持されている様子が確認できます。
Quagga-1# sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 10.0.0.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.1 0 32768 ?
*> 10.0.0.1/32 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.101.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.102.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
Total number of prefixes 7
3. BGPSpeakerサンプルコード
今回のサンプル(sampleBGP.py)は、こんな感じです。
import eventlet # BGPSpeaker needs sockets patched eventlet.monkey_patch() from ryu.services.protocols.bgp.bgpspeaker import BGPSpeaker def dump_remote_best_path_change(event): print 'the best path changed:', event.remote_as, event.prefix,\ event.nexthop, event.is_withdraw if __name__ == "__main__": speaker = BGPSpeaker(as_number=65002, router_id='10.0.0.2', best_path_change_handler=dump_remote_best_path_change, ssh_console=True) speaker.neighbor_add('192.168.200.1', 65001) prefix = '192.168.101.0/24' speaker.prefix_add(prefix='192.168.101.0/24', next_hop='192.168.201.1') eventlet.sleep(3000)
4. 動作確認結果
「sampleBGP.py」サンプルコードの実行は、ルート権限で行います。
BGPルータ(Quagga1)で保持しているPrefix情報を受信した様子が確認できました。
$ sudo python ./sampleBGP.py the best path changed: 65001 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 10.0.0.1/32 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 192.168.200.0/24 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 192.168.100.0/24 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 192.168.0.0/24 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 172.16.102.0/24 192.168.200.1 False the best path changed: 65001 172.16.101.0/24 192.168.200.1 False
再度、BGPルータ(Quagga1)でBGPテーブルを参照してみると、「192.168.101.0」経路が追加されている様子が確認できました。
Quagga-1# sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 10.0.0.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.1 0 32768 ?
*> 10.0.0.1/32 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.101.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.102.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.101.0 192.168.200.100 0 65002 i
*> 192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
Total number of prefixes 8BGPSpeakerでは、豊富なAPIが提供されているので、BGP自体を動作されるのは、それほど難しいことではありません。
でも、BGPSpeakerが、やってくれることは、あくまでもBGP制御によるPrefix経路の配布管理です。
実際に、PC端末がインターネットと通信できるようなデータプレーン構築機能は有しておりません。
そこで、これまでのOpenFlow簡易ルータとのBGP連携により、データプレーン構築を含めた動作確認にチャレンジしてみます。
◆BGP版OpenFlow簡易ルータ構築
PC端末がインターネット通信できるようにするためには、途中経路のデータプレーンを適切に構築する必要があります。そこで、OpenFlow簡易ルータでのBGP/OpenFlow連携の機能拡充を行いました。これにより、BGPSpeakerが対向BGPルータからPrefix経路情報を取得した場合、OpenFlowスイッチ上にFlowエントリを設定できるようになります。
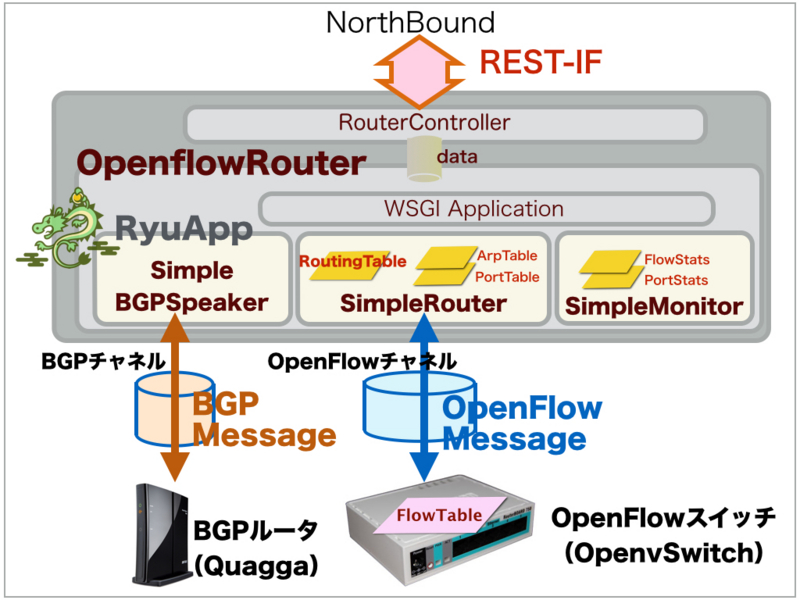
1. プログラムの入手
BGP版OpenFlow簡易ルータのプログラム一式を以下のサイトからダウンロードできます。
Release OpenFlow簡易ルータ(BGP統合版) · ttsubo/simpleRouter · GitHub
あくまでも、BGP/OpenFlow実装テクニックの学習素材なので、実用性を想定した実装は一切行っておりません... (^_^;)
2. 環境構築
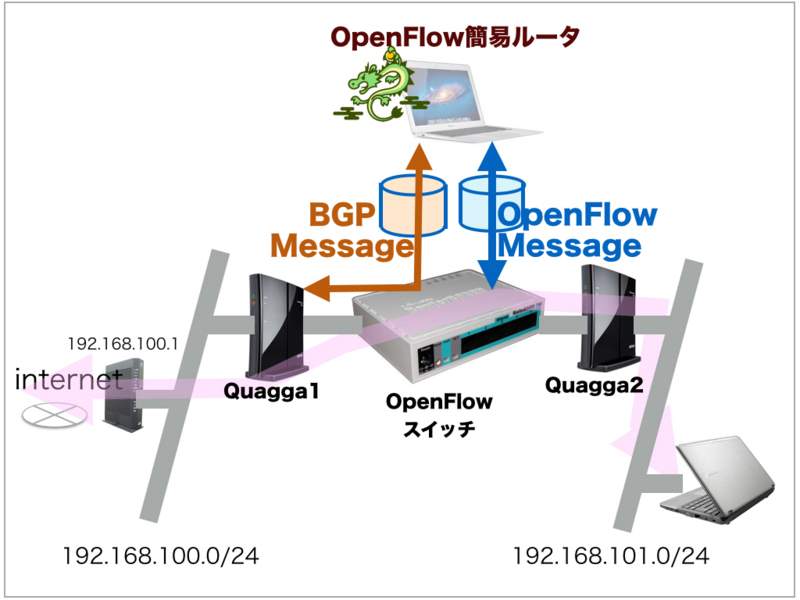
実際の環境構築として、OpenFlowスイッチは、RB750GLを使用しました。実際の構築手順は、こちらのブログ記事を参考にしてください。
RouterBOARD (RB750GL)のOpenFlow化へのチャレンジ 〜OpenvSwitch構築手順メモ編〜 - SDN開発エンジニアを目指した活動ブログ
なお、実際のLANケーブル結線は、こんな感じです。
あと、RB750GL上にて、LANケーブル結線に応じたOVSポート追加を行います。
root@OpenWrt:~# ovs-vsctl add-port br0 eth0.4
OpenFlowスイッチでのOpenFlowポート設定は、こんな感じです。
root@OpenWrt:~# ovs-ofctl dump-ports-desc br0 --protocols=OpenFlow13
OFPST_PORT_DESC reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x2):
1(eth0.2): addr:d4:ca:6d:73:14:8b
config: 0
state: 0
current: 1GB-FD AUTO_NEG
advertised: 1GB-FD
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 1000 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
2(eth0.3): addr:d4:ca:6d:73:14:8b
config: 0
state: 0
current: 1GB-FD AUTO_NEG
advertised: 1GB-FD
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 1000 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
3(eth0.4): addr:d4:ca:6d:73:14:8b
config: 0
state: 0
current: 1GB-FD AUTO_NEG
advertised: 1GB-FD
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 1000 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
LOCAL(br0): addr:d4:ca:6d:73:14:8b
config: PORT_DOWN
state: LINK_DOWN
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps maxつぎに、Ryuコントローラ側の設定です。
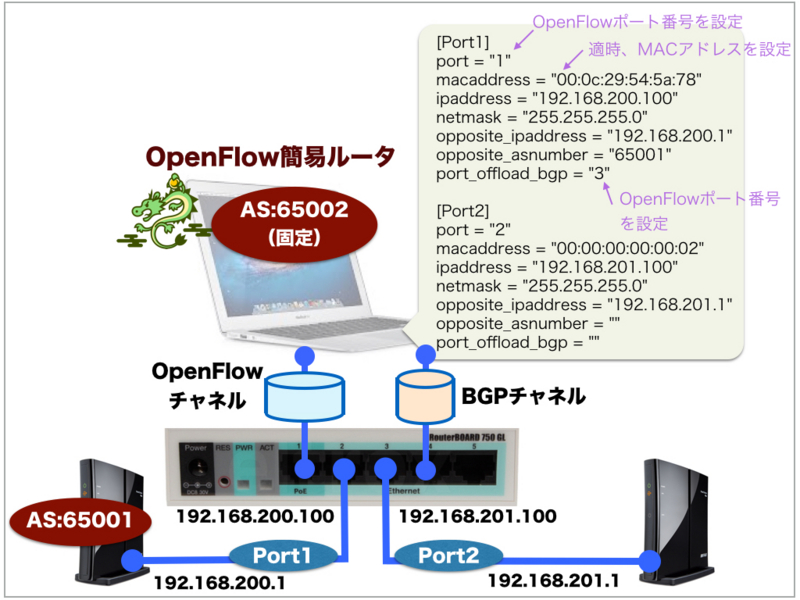
まずは、BGPルータとの隣接関係を構築するために、新たに、NIC追加を行い、IPアドレス"192.168.200.100"を付与します。
さらに、OpenFlow簡易ルータ構成に関わるOpenFlow.ini ファイルの初期設定を行います。
"Port1"のmacaddressとして設定する値は、さきほどのIPアドレス"192.168.200.100"として追加したNICに割り当てられているMACアドレスです。動作させる環境に応じて適切なMACアドレスを設定してください。
$ cd simpleRouter-0.2/rest-client/ $ vi OpenFlow.ini [Port1] port = "1" macaddress = "xx:xx:xx:xx:x:xx" ipaddress = "192.168.200.100" netmask = "255.255.255.0" opposite_ipaddress = "192.168.200.1" opposite_asnumber = "65001" port_offload_bgp = "3" [Port2] port = "2" macaddress = "00:00:00:00:00:02" ipaddress = "192.168.201.100" netmask = "255.255.255.0" opposite_ipaddress = "192.168.201.1" opposite_asnumber = "" port_offload_bgp = "" [Gateway] ipaddress = "192.168.200.1"
3. 実行開始
BGP版OpenFlow簡易ルータをルート権限で起動します。
$ sudo ryu-manager openflowRouter.py
loading app openflowRouter.py
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
creating context wsgi
instantiating app None of SimpleMonitor
creating context monitor
instantiating app None of SimpleBGPSpeaker
creating context bgps
instantiating app openflowRouter.py of OpenflowRouter
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
API method core.start called with args: {'router_id': '10.0.0.2', 'label_range': (100, 100000), 'waiter': <ryu.lib.hub.Event object at 0x1058a6450>, 'local_as': 65002, 'bgp_server_port': 179, 'refresh_max_eor_time': 0, 'refresh_stalepath_time': 0}
(27034) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
starting ssh server at localhost:4990さらに別ターミナルから、REST-IF経由で、構成情報の設定を行います。
$ cd simpleRouter-0.2/rest-client/
$ ./post_interface.sh
======================================================================
create_interface
======================================================================
/openflow/0000000000000001/interface
{
"interface": {
"port": "1",
"macaddress": "40:6c:8f:59:31:af",
"ipaddress": "192.168.200.100",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"opposite_ipaddress": "192.168.200.1",
"opposite_asnumber": "65001",
"port_offload_bgp": "3"
}
}
----------
reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
header: Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
header: Content-Length: 243
header: Date: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 05:28:47 GMT
----------
{
"interface": {
"macaddress": "40:6c:8f:59:31:af",
"opposite_asnumber": "65001",
"port_offload_bgp": "3",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"opposite_ipaddress": "192.168.200.1",
"ipaddress": "192.168.200.100",
"port": "1"
},
"id": "0000000000000001"
}
======================================================================
create_interface
======================================================================
/openflow/0000000000000001/interface
{
"interface": {
"port": "2",
"macaddress": "00:00:00:00:00:02",
"ipaddress": "192.168.201.100",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"opposite_ipaddress": "192.168.201.1",
"opposite_asnumber": "",
"port_offload_bgp": ""
}
}
----------
reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
header: Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
header: Content-Length: 237
header: Date: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 05:28:52 GMT
----------
{
"interface": {
"macaddress": "00:00:00:00:00:02",
"opposite_asnumber": "",
"port_offload_bgp": "",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"opposite_ipaddress": "192.168.201.1",
"ipaddress": "192.168.201.100",
"port": "2"
},
"id": "0000000000000001"
}
最後に、PC端末を収容しているLANセグメントを対象に、スタティックルーティング設定を行います。
$ ./post_route.sh 192.168.101.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.201.1
======================================================================
create_route
======================================================================
/openflow/0000000000000001/route
{
"route": {
"destination": "192.168.101.0",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"nexthop": "192.168.201.1"
}
}
----------
reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
header: Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
header: Content-Length: 125
header: Date: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 05:29:52 GMT
----------
{
"route": {
"destination": "192.168.101.0",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"nexthop": "192.168.201.1"
},
"id": "0000000000000001"
}OpenFlow簡易ルータで保持しているルーティングテーブル情報を確認してみます。
さきほど設定したスタティックルーティングや、BGPルータから配布されたPrefix情報が確認できました。
$ ./get_route.sh ====================================================================== get_route ====================================================================== /openflow/0000000000000001/route ---------- reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n' header: Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8 header: Content-Length: 1275 header: Date: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 05:31:28 GMT +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ 2014/11/29 14:31:28 : RoutingTable +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ prefix nexthop ------------------ ---------------- 192.168.0.0/24 192.168.200.1 192.168.200.0/24 192.168.200.1 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.200.1 10.0.0.1/32 192.168.200.1 172.16.101.0/24 192.168.200.1 192.168.101.0/24 192.168.201.1 172.16.102.0/24 192.168.200.1 192.168.201.1/32 0.0.0.0 192.168.200.1/32 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.0/24 192.168.200.1
BGPルータ側でのBGPテーブルも確認しておきます。
Quagga-1# sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 10.0.0.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.1 0 32768 ?
*> 10.0.0.1/32 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.101.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 172.16.102.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
*> 192.168.101.0 192.168.200.100 0 65002 i
*> 192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 1 32768 ?
Total number of prefixes 8OpenFlowスイッチ側でのFlowテーブルも確認しておきます。
root@OpenWrt:~# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br0 --protocols=OpenFlow13 OFPST_FLOW reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x2): cookie=0x0, duration=262.466s, table=0, n_packets=140, n_bytes=52980, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=192.168.101.0/24 actions=set_field:00:00:00:00:00:02->eth_src,set_field:16:23:ec:ab:8d:8d->eth_dst,output:2,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=311.750s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=172.16.102.0/24 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=312.754s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=192.168.0.0/24 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=313.758s, table=0, n_packets=146, n_bytes=11754, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=192.168.100.0/24 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=310.746s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=172.16.101.0/24 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=314.763s, table=0, n_packets=25, n_bytes=3496, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=192.168.200.0/24 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=327.431s, table=0, n_packets=129, n_bytes=9677, priority=255,ip,in_port=3,nw_dst=192.168.200.1 actions=output:1 cookie=0x0, duration=327.431s, table=0, n_packets=115, n_bytes=9157, priority=255,ip,in_port=1,nw_dst=192.168.200.100 actions=output:3 cookie=0x0, duration=316.770s, table=0, n_packets=211, n_bytes=31030, priority=1,ip actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=327.432s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=16,ip,nw_dst=192.168.200.100 actions=CONTROLLER:65535 cookie=0x0, duration=315.766s, table=0, n_packets=4, n_bytes=296, priority=15,ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.1 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=322.417s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=16,ip,nw_dst=192.168.201.100 actions=CONTROLLER:65535 cookie=0x0, duration=330.285s, table=0, n_packets=19, n_bytes=1525, priority=0 actions=CONTROLLER:65535 cookie=0x0, duration=327.431s, table=0, n_packets=7, n_bytes=420, priority=255,arp,in_port=1 actions=output:3,CONTROLLER:65535 cookie=0x0, duration=327.433s, table=0, n_packets=4, n_bytes=240, priority=255,arp,in_port=3 actions=output:1,CONTROLLER:65535 cookie=0x0, duration=274.075s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=2,ip,in_port=2,dl_src=16:23:ec:ab:8d:8d,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:02,nw_dst=192.168.200.1 actions=set_field:40:6c:8f:59:31:af->eth_src,set_field:96:9a:9c:c5:74:70->eth_dst,output:1,dec_ttl cookie=0x0, duration=274.075s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=2,ip,in_port=1,dl_src=96:9a:9c:c5:74:70,dl_dst=40:6c:8f:59:31:af,nw_dst=192.168.201.1 actions=set_field:00:00:00:00:00:02->eth_src,set_field:16:23:ec:ab:8d:8d->eth_dst,output:2,dec_ttl
4. 動作確認
ひととおり、PC端末からインターネット通信できるような経路設定が完了したので、さっそく、インターネットにアクセスしてみます。想定どおり、YouTubeを快適にアクセスできました。(BabyMetalのベーシストの超絶テク、いいですよね。)
OpenFlow簡易ルータを通過したトラフィック流量を確認してみました。
$ ./get_flow_stats.sh
======================================================================
get_flowstats
======================================================================
/openflow/0000000000000001/stats/flow
----------
reply: 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n'
header: Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
header: Content-Length: 1158
header: Date: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 05:46:45 GMT
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2014/11/29 14:46:45 : FlowStats
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
inPort ethSrc ethDst ipv4Dst packets bytes
-------- ------------------ ------------------ --------------- -------- --------
1 96:9a:9c:c5:74:70 40:6c:8f:59:31:af 192.168.201.1 0 0
2 16:23:ec:ab:8d:8d 00:00:00:00:00:02 192.168.200.1 0 0
* * * 192.168.101.0 49038 67791018
* * * 192.168.100.0 363 28728
* * * 172.16.102.0 0 0
* * * 0.0.0.0/0 18161 2768420
* * * 192.168.200.0 49 6952
* * * 10.0.0.1 4 296
* * * 192.168.0.0 0 0
* * * 172.16.101.0 0 0
◆おわりに
SDN/OpenFlow実装テクニックにより、BGP/OpenFlow連携によるデータプレーン構築が可能であることが確認できました。
最近のSDNテクノロジでは、集中制御から分散制御に、話題がシフトしている気がします。
今後は、「SDN分散制御における中核技術としてのBGP拡張が、どこまで具現化していくのか?」を意識しながら、Ryu BGPSpeakerの活用をいろいろと考えていきたいです。